National Electricity Market and Rules
The National Electricity Market is where the wholesale power exchange between electricity producers and consumers takes place.
The National Electricity Market (NEM) uses a pooled system that combines and schedules output from all generators in real-time to meet the electricity demands of consumers.
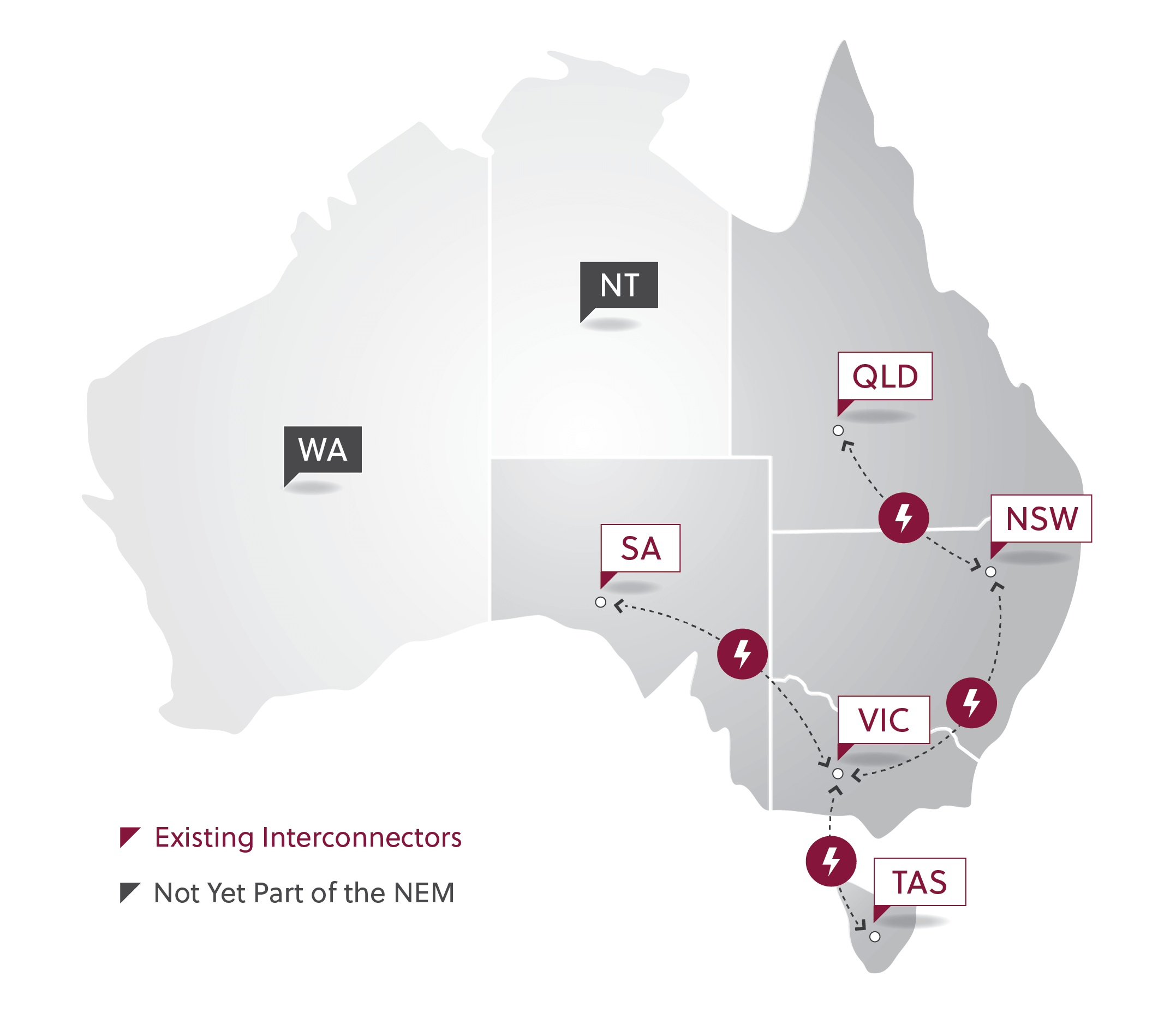
The NEM operates across an interconnected power system. Interconnected regions largely follow the state boundaries of the participating jurisdictions, including Queensland (Qld), New South Wales (NSW), Victoria (Vic), South Australia (SA) and Tasmania (TAS).
The power grids of Western Australia (WA) and the Northern Territory (NT) operate independently.
History and Management
The NEM began operating across the eastern seaboard states of Australia in 1998. Tasmania physically joined the market in 2005 through an unregulated interconnection with Victoria, named Basslink. All other Australian interconnectors are operated as regulated links.
The NEM is overseen by three main market institutions:
- The Australian Energy Market Commission (AEMC), responsible for rule making and market development.
- The Australian Energy Regulator (AER), responsible for economic regulation and rule enforcement.
- The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO), responsible for market and power system operation, including maintaining a required amount of electricity in reserve, coordinating how the generated electricity is dispatched, and determining the spot price and financial settlement of the market.
These institutions are responsible to the Council of Australian Governments (COAG) through the Energy Council, consisting of the federal, state and territory energy ministers. The Energy Council is responsible for setting the policy and regulatory framework for the NEM.
The NEM operates within the framework of the National Electricity Rules under joint legislation enacted by the participating States and Territories.
The Rules are maintained and developed by the AEMC and enforced by the AER.
ElectraNet and the NEM
ElectraNet has been a part of NEM since it began in 1998. We are the principal Transmission Network Service Provider (TNSP) and System Control Operator for South Australia’s high-voltage electricity transmission network.
We plan, develop and operate South Australia’s electricity transmission network in accordance with the mandated reliability and security standards set out in the Rules and the South Australian Transmission Code.
We also comply with the specific power system performance and quality of supply standards that are required.
Fast Facts about the NEM:
- The NEM started as a wholesale spot market for electricity in December 1998.
- The NEM has around 51,000 km of transmission lines and cables.
- The NEM supplies about 200 terawatt hours of electricity to businesses and households each year.
- The NEM supplies approximately nine million customers.
- The NEM has a total electricity generating capacity of around 45,000 MW.
To find out more about the market and how it operates, visit the website of the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO).